Sinus Bradycardia
Sinus Bradycardia is a Sinus Rhythm with a rate less than 60bpm and is otherwise identical to Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR). This slow rate results in long RR Intervals on the EKG tracing and fewer complexes per minute.
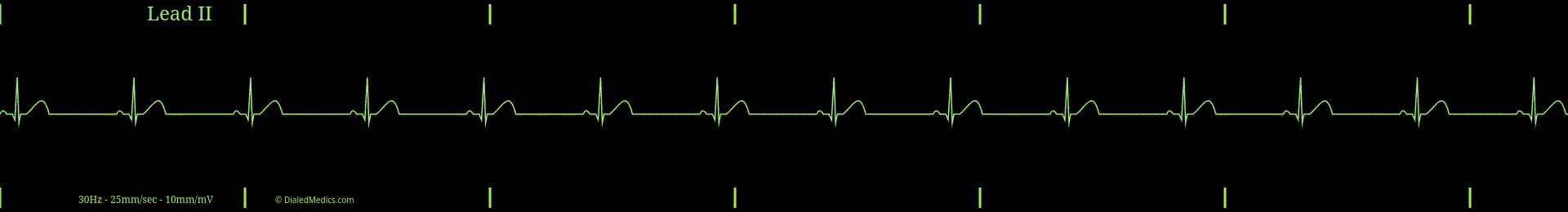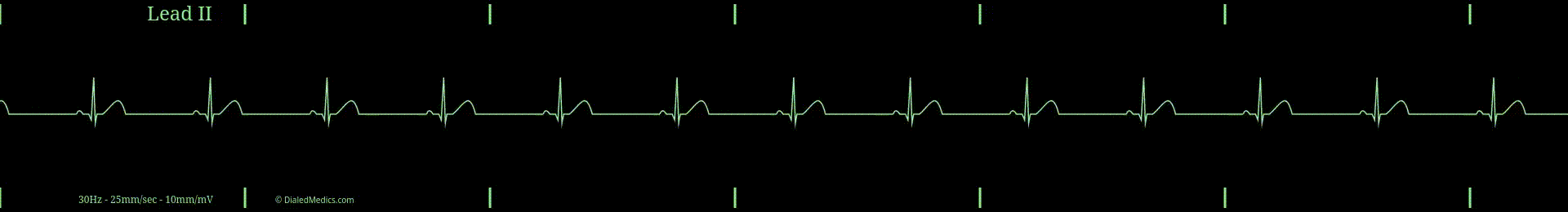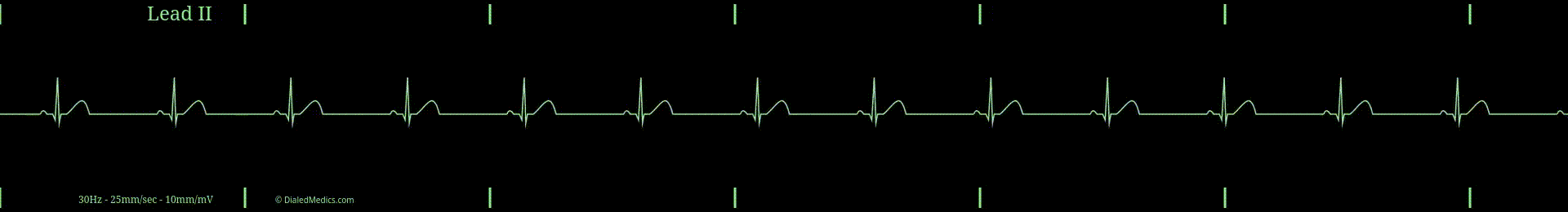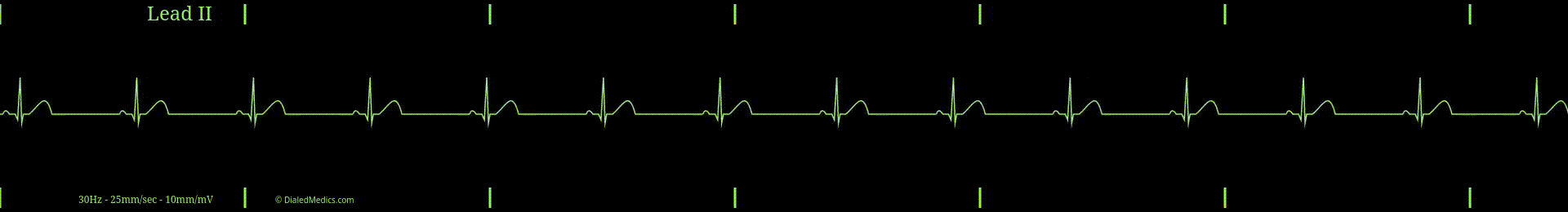
Being in the category of Sinus Rhythms, Sinus Bradycardia has the same P-QRS-T pattern seen in Normal Sinus Rhythm. The brady in Sinus Bradycardia means slow. A Sinus Rhythm is slow when its heart rate is less than 60 beats per minute (bpm): the slowest rate of NSR.
Once a tracing is identified as a Sinus Rhythm with a heart rate (HR) less than 60bpm, it can be called Sinus Bradycardia. Sinus Bradycardia means:
An EKG rhythm starting at the SA Node with a rate below 60 which follows the expected electrical path through the heart.
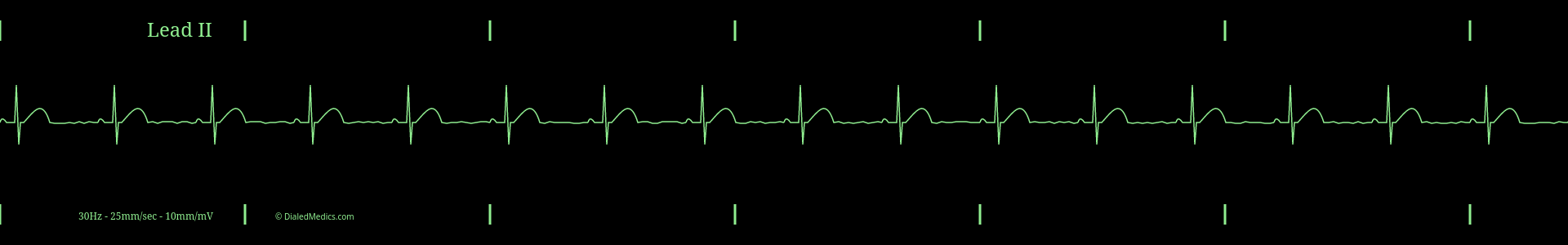
Defining Characteristic of Sinus Bradycardia in Lead II
The only differentiating factor of Sinus Bradycardia from other Sinus Rhythms is the heart rate:
- RR Intervals greater than 1sec (25mm) [5 large boxes] in duration.
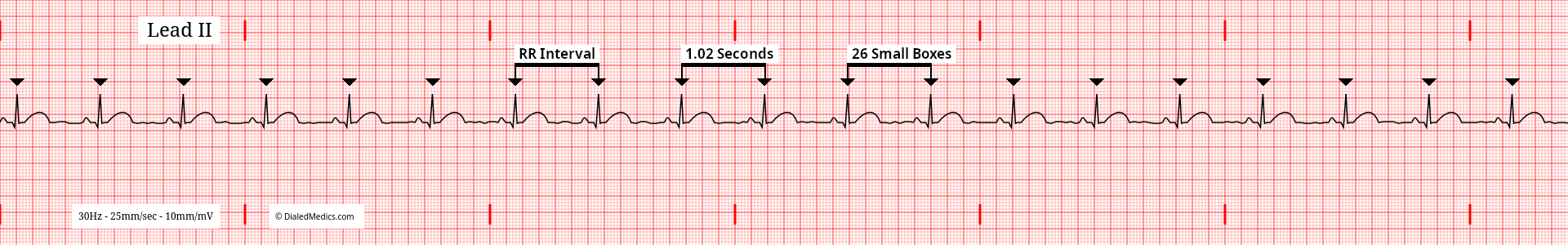
In the below example (fig. 1) R Waves are marked with black triangles and several RR Intervals are labeled. The distance between two R Waves is the RR Interval. The minimum RR Interval that a Sinus Bradycardia can have is 26mm (1.2sec) [26 small boxes]. A shorter RR Interval would result in a HR of 60bpm or more.
Extremely Slow Rates of Sinus Bradycardia
When a Sinus Bradycardia becomes too slow to reasonably produce significant cardiac output, it is defined as an Agonal Rhythm. Different educational organizations and textbooks have different definitions for the specific rate at which a rhythm becomes agonal. The example below (fig. 2) shows a Sinus Bradycardia with a HR of 4bpm, which is generally considered to be an Agonal Rhythm.
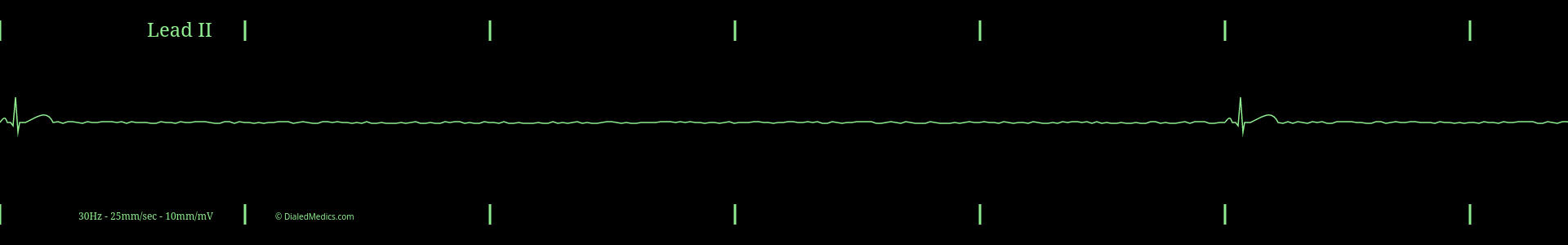
There is no official number for how slow a Sinus Bradycardia must be to become agonal. Some textbooks define Agonal Rhythm as rates less than 20 or as low as 6. Reference your textbook, instructor, or local protocols for the specific cutoff in your area.
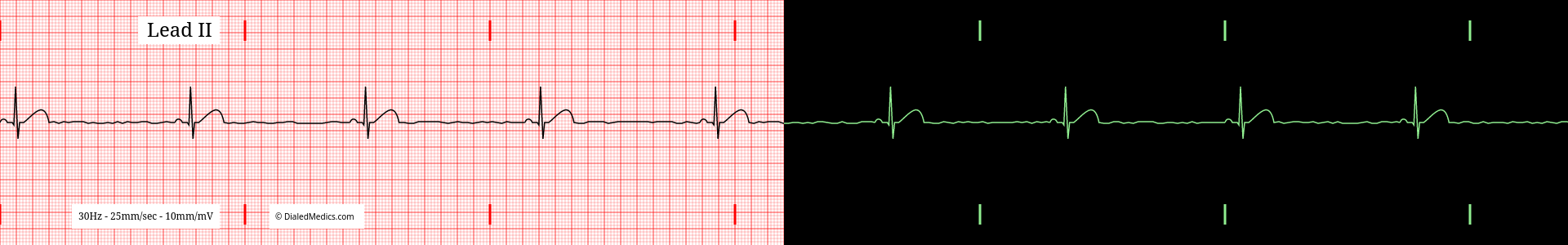
Below are several more examples of Sinus Bradycardia presented as monitor captures as well as on ECG graphs.
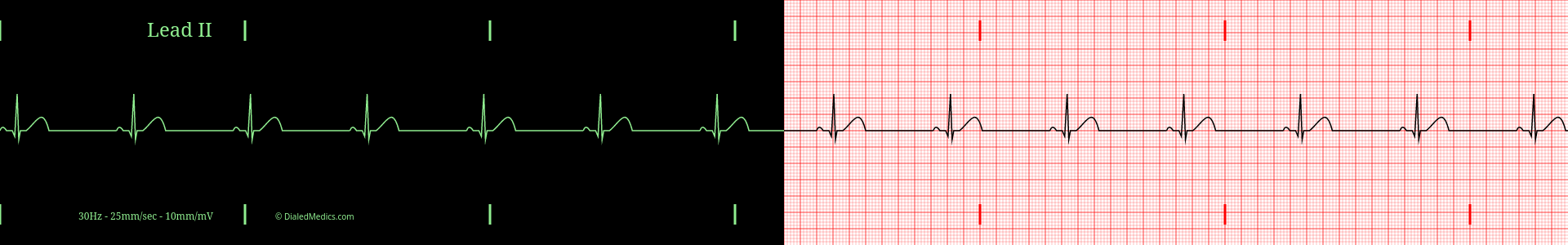
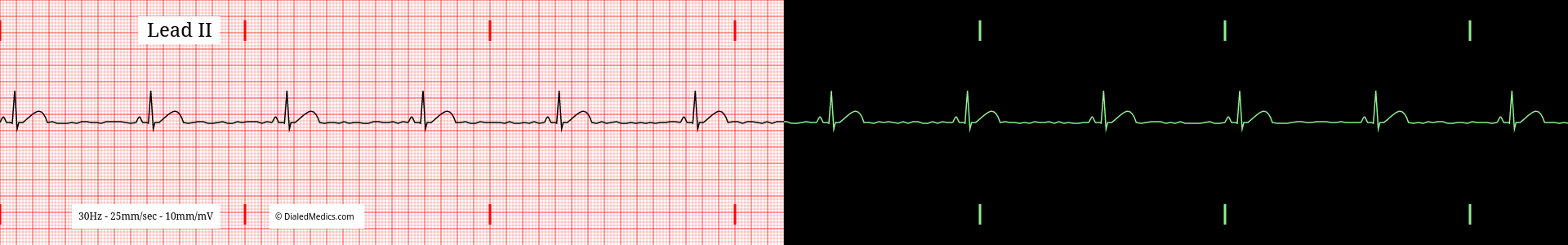
After becoming confident in identifying EKGs as Sinus Bradycardia you can continue by learning about the faster rate of Sinus Rhythm: Sinus Tachycardia, or review Normal Sinus Rhythm. Head back to our EKG Rhythm Index to find information on another ECG. Otherwise, practice interpreting novel EKGs with our EKG Generator:
Basic EKG App
Our Basic EKG Generator is free with an email signup and covers Normal Sinus Rhythm along with common arrhythmia.
Pro EKG App
Our Pro EKG Generator covers over 40 different rhythm categories, multiple display options, has Quiz and Simulation modes, and more! Try it out for just $5 for a month.
