Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR)
Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) is the expected rhythm on an EKG in patients without pathophysiology. It represents the normal electrical cycle of the heart, which was discovered once a tool capable of detecting it was invented: the electrocardiogram (EKG/ECG).
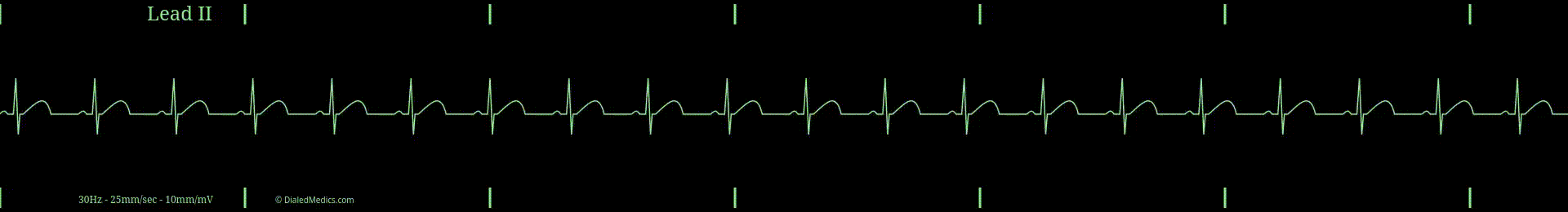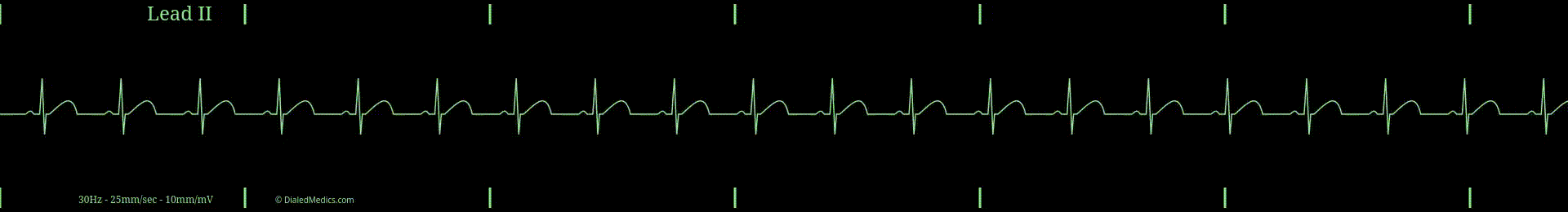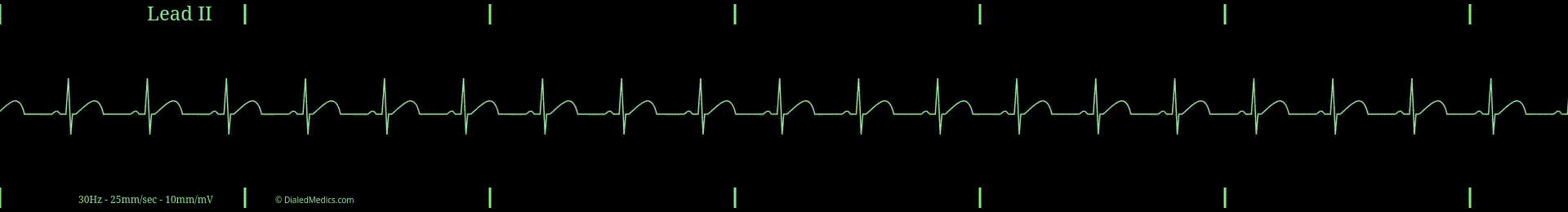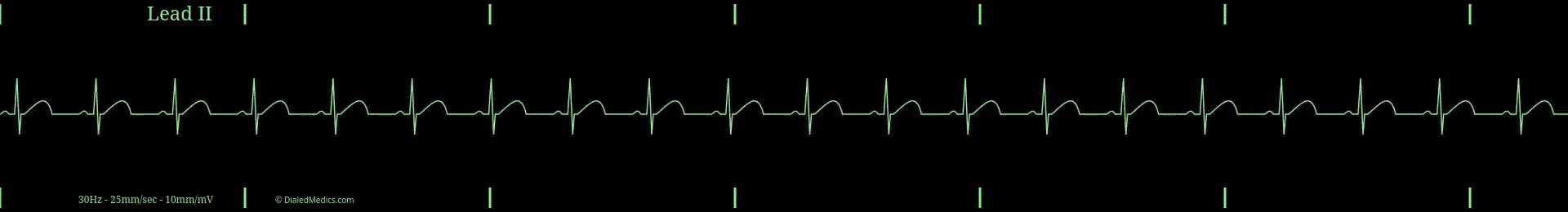
Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) and Regular Sinus Rhythm (RSR) are synonymous. In clinical settings, you can use and will hear both interchangeably, with Normal Sinus Rhythm being more common.
Many concepts in EKG interpretation are defined in terms of the way a rhythm or wave differs from how it is found in NSR. Understanding why an EKG tracing is not Normal Sinus Rhythm gets you most of the way to identifying what dysrhythmia a tracing is.
Clinically, the terms dysrhythmia and arrhythmia are synonymous and refer to all cardiac rhythms EXCEPT Normal Sinus Rhythm.
NSR is a type of Sinus Rhythm and the prototypical example of it. Sinus Rhythms, as a category, include all rhythms that originate from the Sino-Atrial Node (SA Node / SAN), making it the primary pacemaker of the rhythm. The hallmark of sinus-originating rhythms are upright, uniform P Waves (in Lead II) at the beginning of the repeating organized complex, followed by a QRS-T pattern (described below).
The term normal in Normal Sinus Rhythm refers to the expected 'normal' rate of the SA Node. In the average healthy heart, the SA Node will create an electrical action potential between 60 and 99 times per minute; therefore a NSR should have a heart rate (HR) between 60 and 99.
When an EKG tracing meets these criteria —sinus-originating, fixed P-QRS-T repeating pattern, and HR between 60 and 99— it can be called Normal Sinus Rhythm.
Normal Sinus Rhythm means:
An EKG rhythm starting at the SA Node with a rate between 60 and 99 which follows the expected electrical path through the heart.
Defining Characteristics* of NSR in Lead II
- RR Intervals greater than 0.60sec (15mm) [3 large boxes] in duration.
- RR Intervals less than 1sec (25mm) [5 large boxes] in duration.
- Equal RR Intervals between all complexes.
- Less than 0.12sec (3mm) [3 small boxes] in duration.
- Less than 2.5mm (0.25mV) [2.5 small boxes] in amplitude.
- Greater than 0.12sec (3mm) [3 small boxes] in duration.
- Less than 0.20sec (5mm) [1 large box] in duration.
- Less than 0.12sec (3mm) [3 small boxes] in duration.
- Approx. 0.42sec (10.5mm) [10.5 small boxes] in duration.†
- Less than 5mm (0.5mV) [1 large box] in amplitude.
* Changes in some features may not categorize a rhythm from NSR to something else and instead be mentioned after, such as: NSR with a First Degree Heart Block or NSR with a Left Bundle Branch Block. Specific cases are noted below.
† QT Intervals are variable with HR, age, and sex. The measured QT Interval is used to calculate the corrected QT Interval, which is then compared to demographic norms. In general, the corrected QT Interval should be between 350ms and 450ms. QT Intervals should be measured on a 12L EKG rather than a rhythm tracing.
Rate of a Normal Sinus Rhythm
The heart rate of Normal Sinus Rhythm is between 60 and 99 beats per minute. Slower than 60bpm would be Sinus Bradycardia and faster than 99bpm would be Sinus Tachycardia.
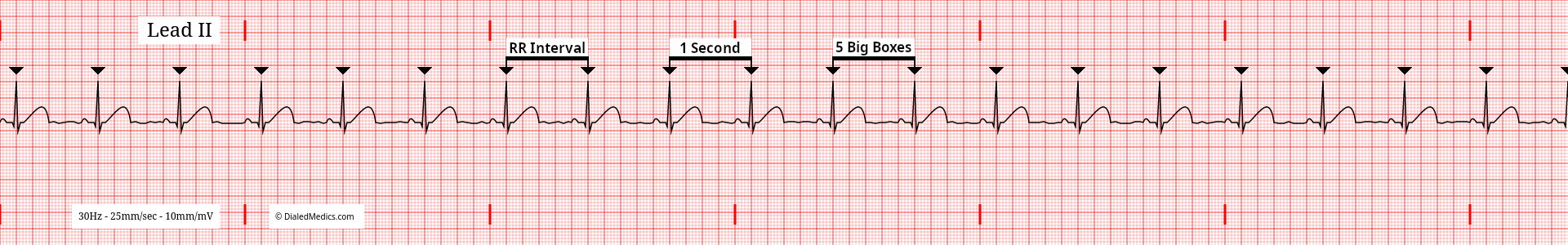
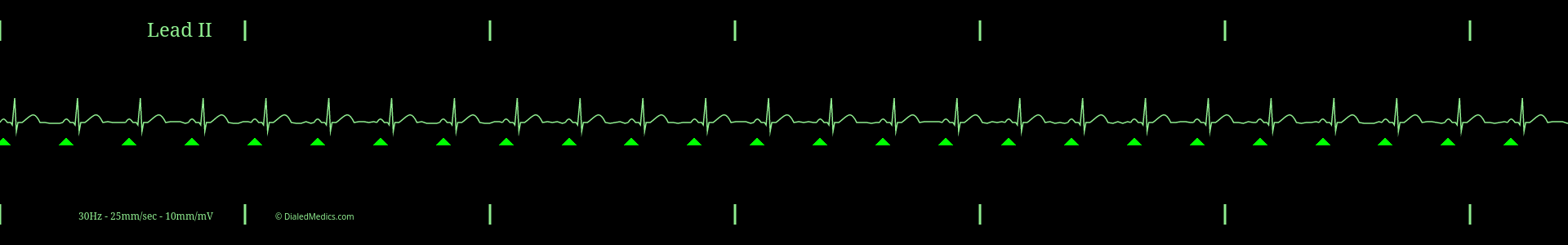
In the above example (fig. 1) R Waves are marked with black triangles. The distance between two R Waves is the RR Interval. The maximum RR Interval that a Normal Sinus Rhythm can have is 25mm (1sec) [5 large boxes]. A longer RR Interval would result in a bradycardic HR of less than 60bpm.
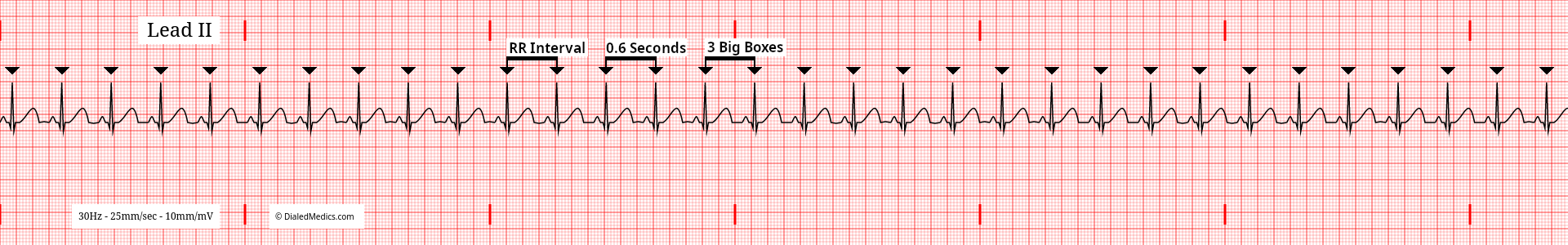
In this example (fig. 2) R Waves are also marked with black triangles and several RR Intervals are labeled. The minimum RR Interval that a Normal Sinus Rhythm can have is 15mm (0.60sec) [3 large boxes]. A shorter RR Interval would result in a tachycardic HR of 100bpm or more.
A Normal Sinus Rhythm MUST have an RR Interval between the two above examples (five large boxes and three large boxes.)
Don't let the word 'normal' in NSR fool you into thinking that all rates of NSR are clinically normal in a patient. While a HR of 90 may be called Normal Sinus Rhythm, whether it is clinically relevant depends on the status of the patient. A HR of 90 could be irrelevant, a sign of anxiety or stress, or a sign of underlying pathophysiology. 'Normal' in this case is just part of the name of this ECG rhythm.
Expected Rhythm of NSR
Normal Sinus Rhythm is a regularly regular rhythm. This means that it has a regular beat to it like a metronome. Every beat comes at a fixed time interval, with no pattern or variation.
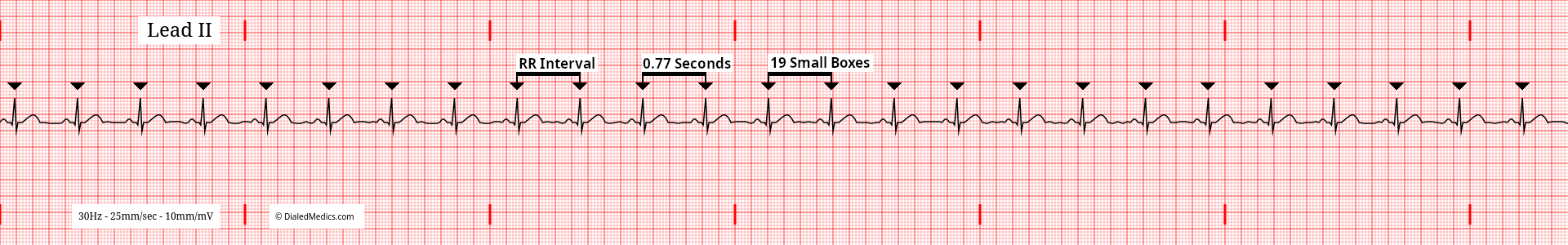
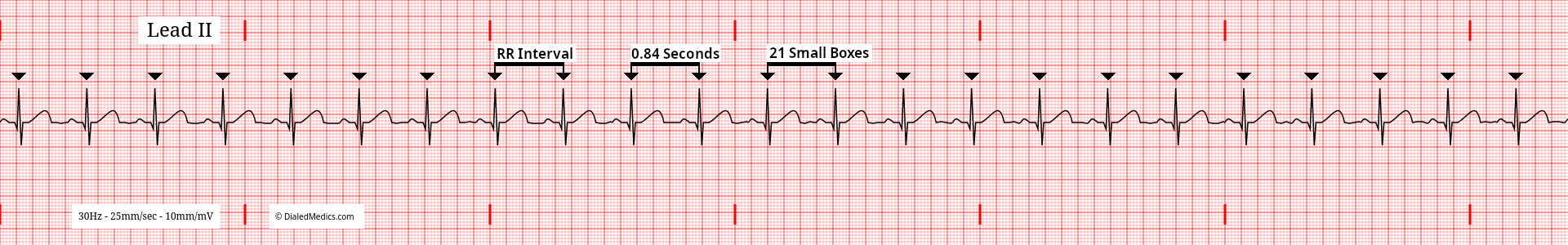
The RR Intervals of a Normal Sinus Rhythm should be equal to each other in any given tracing. In the above ECG (fig. 3) the RR Interval is 19mm (small boxes) or 77ms and throughout the tracing remains the same. The below tracing (fig. 4) has an RR Interval of 21mm (small boxes) or 84ms, which is also equal throughout. The defining factor of a regularly regular rhythm is that the RR Intervals are constant.
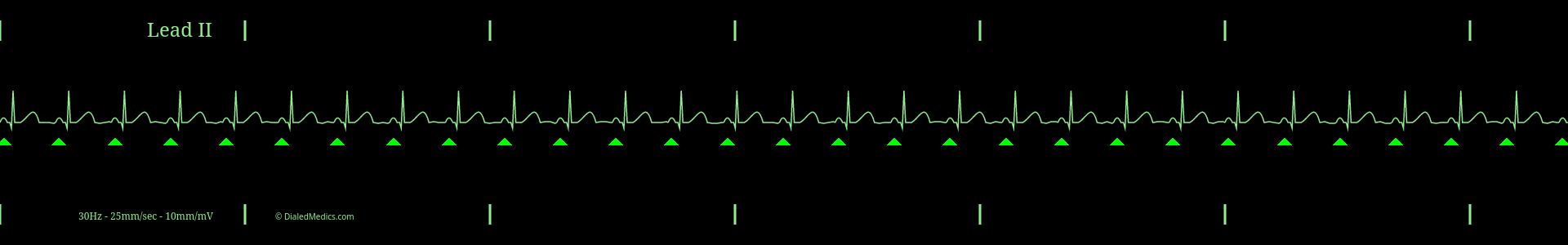
In practice, no rhythm is perfectly regular. When interpreting an EKG as Normal Sinus Rhythm it is appropriate to ignore minor irregularity of +/- less than 1mm.
P Waves in Normal Sinus Rhythm
P Waves in Normal Sinus Rhythm will be the first feature of the repeating pattern of organized electrical activity. P Waves represent movement of the atrial action potential from its origin (SA Node) to the Atrio-Ventricular Node (AVN) through the atria. They are upright, uniform, and always followed by QRS Complexes (discussed below.) In the following example (fig. 5), P Waves are marked with green triangles. The P Waves have positive deflections above baseline (upright), are identical from one complex to the next (uniform), and all precede QRS Complexes.
P Waves in NSR should be less than 0.12sec (3mm) [3 small boxes] in duration and less than 2.5mm (0.25mV) [2.5 small boxes] in amplitude.
The three primary criteria for P Waves in Normal Sinus Rhythm (upright, uniform, preceding QRS complexes) are all expected for specific reasons:
Upright
Upright P Waves (in Lead II) indicate that atrial depolarization is moving generally from the patients upper right (SA Node in the right atrium) to the lower left (Atrio-Ventricular Junction). The positive deflection from baseline hints at the sinus origin of Normal Sinus Rhythm.
Uniform
Sinus P Waves should be uniform throughout a tracing. In the below tracing (fig. 6) P Waves have been marked with green triangles; notice how the morphology of the P Wave does not change from one to the next. P Waves being uniform mean that the electrical cycles are originating from the same place and following the same path.
Preceding QRS Complexes
Normal Sinus Rhythm should always have a QRS Complex after every P Wave. If any P Waves are present without a following QRS Complex the tracing is not Normal Sinus Rhythm.
PR Interval in Normal Sinus Rhythms
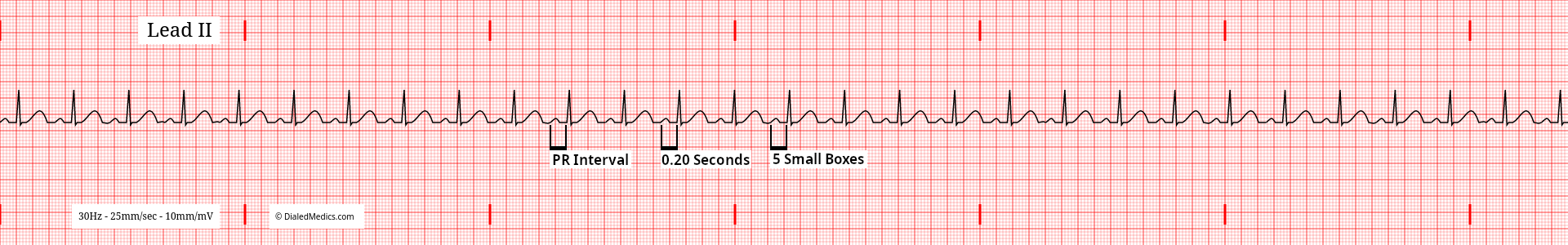
The term PR Interval is a convention. Measuring the PR Interval starts at the beginning of the P Wave and ends at the first deflection of the QRS Complex, not the R Wave. The morphology of the QRS Complex and the presence of Q Waves do not alter that measurement. The PR Interval ends at the first deflection (onset of the QRS) after the P Wave.
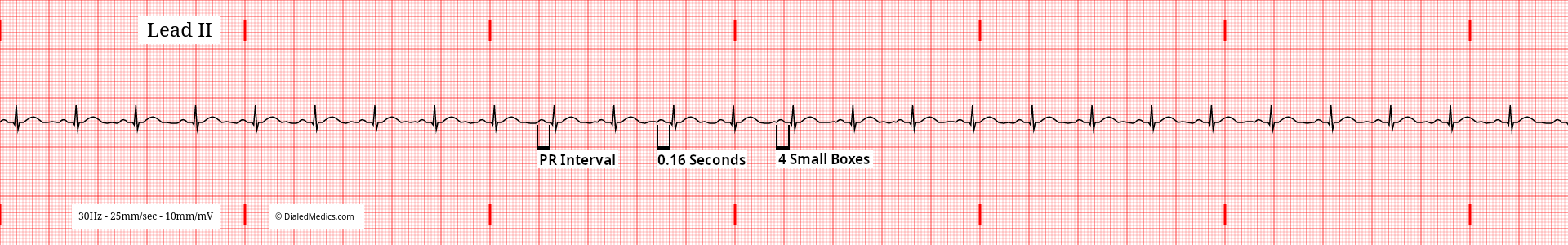
The PR Interval in NSR should be greater than or equal to 0.12sec (3mm) [3 small boxes] and less than or equal to 0.20sec (5mm) [1 large box]. This duration represents both atrial depolarization (P Wave) and the AV Node pause (PR Segment). Like the P Wave, the PR Interval should be fixed (the same in all complexes of the rhythm.) In the examples above and below (fig. 7, fig. 8), we see normal PR Intervals of 160ms and 200ms respectively, which remain the same in every complex.
Changes in the PR Interval don't necessarily change the name of a tracing which otherwise meets NSR criteria. A PR Interval shorter than described (less than 3mm) would be called Normal Sinus Rhythm with [ventricular] Pre-Excitation. While NSR with a longer than described (greater than 5mm) PR Interval is Normal Sinus Rhythm with a First Degree Heart Block.
The QRS Complex of NSR
The name QRS Complex (like PR Interval) is a convention. A QRS Complex does not need to contain Q, R, & S Waves. QRS Complex, in rhythm interpretation, refers to whatever morphology ventricular depolarization creates on a tracing. In 12 Lead EKG interpretation the QRS may be addressed more specifically by Q, R, and S waves, but as a general rule, QRS Complex will be understood to mean the complex of ventricular depolarization.
The key factor of QRS Complexes in Normal Sinus Rhythm is that they are present after every P Wave. The QRS Complex begins with the first deflection (positive or negative) after the P Wave and should be a maximum of 0.12sec (3mm) [3 small boxes] in duration. In the below example (fig. 10) every P Wave is followed by a QRS Complex with a normal duration of 80ms.
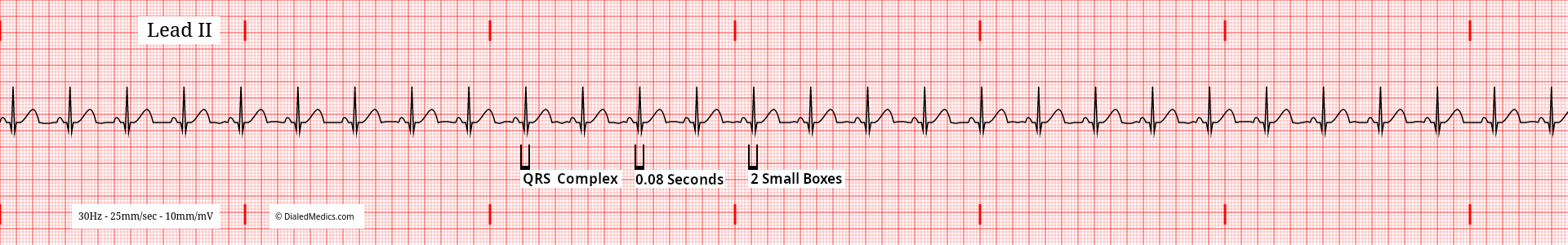
Like the PR Interval, the duration of the QRS Complex exceeding the 3mm normal does not change a Normal Sinus Rhythm interpretation. Instead, depending on the specific morphology of the QRS, additional information is included after; e.g., Normal Sinus Rhythm with a Left / Right Bundle Branch Block. Being less specific, such a rhythm (with a QRS Complex wider than 3mm) could be called a Normal Sinus Rhythm with a Ventricular Conduction Delay.
QT Interval in Normal Sinus Rhythm
The QT Interval should be approximately 0.44sec (11mm) [11 small boxes] in NSR. The duration of any given QT Interval depends on the patients age, sex, and HR, and needs to be calculated into a corrected QT Interval for evaluation. Exact measurements should be made on a 12 Lead EKG, not a rhythm strip or monitor screen. Below (fig. 10) a tracing showing NSR with a HR of 64bpm and a measured QT Interval of 440ms is shown, which calculates to a corrected QT Interval of 454ms. Normal ranges of QT Intervals vary based on patient demographics, but are generally between 350ms and 450ms.
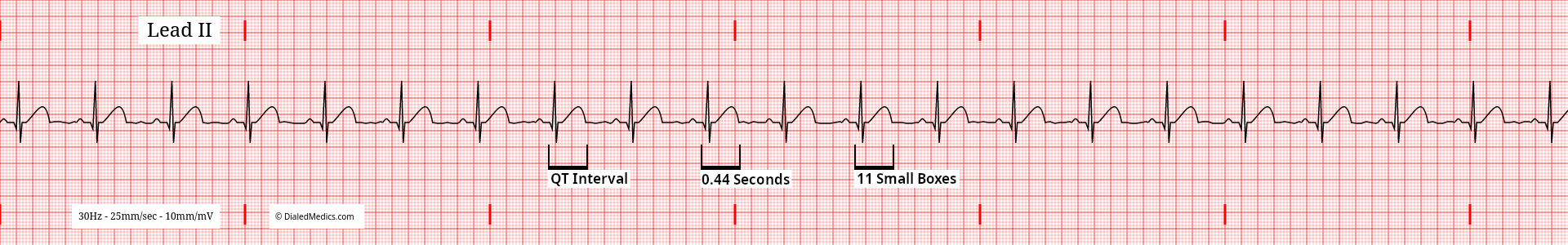
QT Interval abnormalities are another feature that can be described after the title NSR rather than indicating a different rhythm. For example, an extended QT Interval (calculated based on the sex, age, and HR of the patient and measured on a 12 Lead) on a tracing which otherwise meets NSR criteria would be described as Normal Sinus Rhythm with a Long QT Interval.
T Waves of Normal Sinus Rhythm
The T Wave is the final feature of the repeating pattern in NSR. T Waves are expected to be less than 5mm (0.5mV) [5 small boxes], present after every QRS Complex, upright, and uniform. They represent the repolarization wave of the ventricles. Below is an example (fig. 11) of normal T Waves in a NSR tracing, marked with green arrows.
As we have seen in several other features, abnormalities of the T Wave are mentioned after Normal Sinus Rhythm and don't change a tracings primary name, e.g., Normal Sinus Rhythm with Inverted T Waves.
The Repeating Pattern in NSR
After the T Wave there will be a section of baseline (called the TP Segment) followed by the P Wave of the next complex. This repeating pattern of organized electrical activity (P-QRS-T) meeting the criteria discussed above is the hallmark of a Normal Sinus Rhythm.
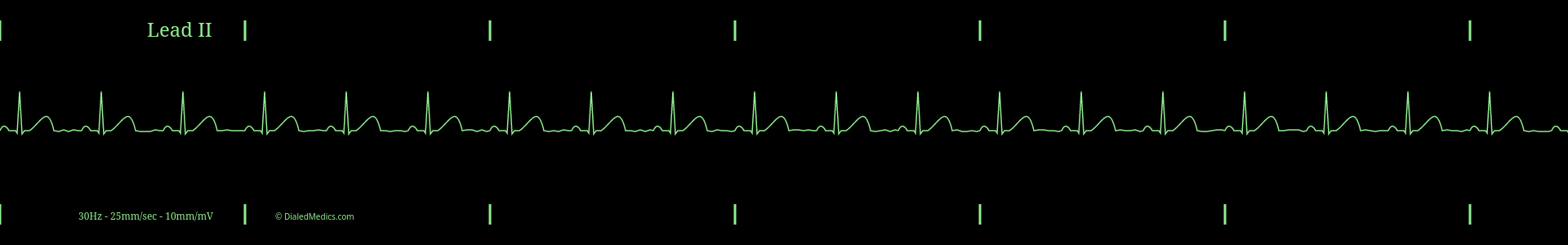
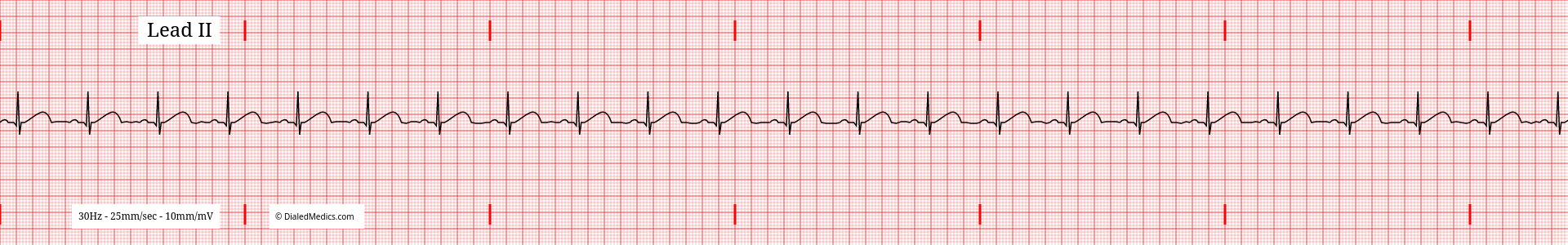
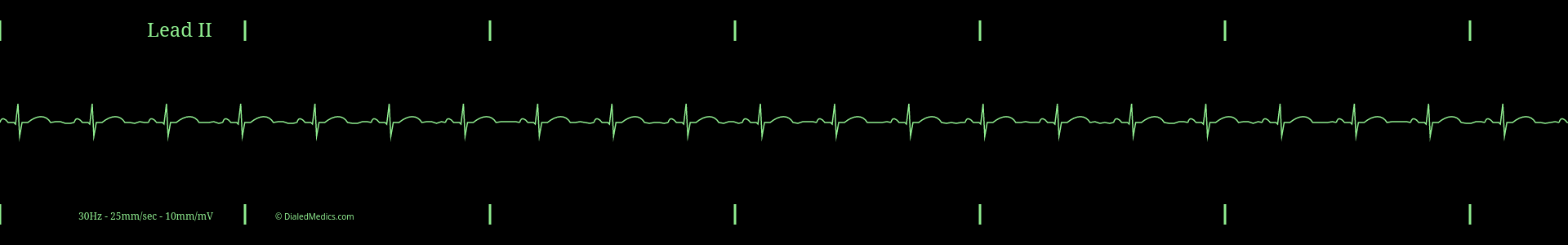
Below are several more examples of Normal Sinus Rhythm presented as monitor captures as well as EKG tracings.
After becoming confident in identifying EKG rhythms as Normal Sinus Rhythm or not, you can continue by learning about specific dysrhythmia such as: Sinus Tachycardia, Sinus Bradycardia, or Sinus Arrhythmia. Or, head back to our EKG Rhythm Index to find information on another rhythm Otherwise, practice interpreting novel EKGs with our EKG Generator:
Basic EKG App
Our Basic EKG Generator is free with an email signup and covers Normal Sinus Rhythm along with common arrhythmia.
Pro EKG App
Our Pro EKG Generator covers over 40 different rhythm categories, multiple display options, has Quiz and Simulation modes, and more! Try it out for just $5 for a month.
